Interoperability in Healthcare – How to Achieve it?
February 24, 2021The role of digitization in the healthcare industry has been significant over the past few years. Leveraging digital software and hardware, doctors have been successfully treating their patients with more care and precision. However, despite the use of tremendous technologies, healthcare systems are still not fully benefiting from these digital systems.
After several years of digital transformations, healthcare interoperability still struggles to earn its place in the industry. Healthcare interoperability can hugely impact the workflow of hospitals by reducing medical error rates, enhancing patient experience, and lowering healthcare costs. This article will take you through some of the advantages of implementing interoperability in healthcare and how to achieve it in your medical organization. Let’s begin!
What is Healthcare Interoperability?
To start with, we shall first understand what interoperability in healthcare means. It is the ability of distinct software applications and information systems to communicate and exchange data between the systems that help provide critical insights for better working of the overall processes.
Interoperability in healthcare can be further divided into four classifications:
● Foundational Interoperability
This is the basic form of interoperability in healthcare. It focuses on transferring data from one information system to another. The information received by one system can only be interpreted when the user tries to access it.
● Structural Interoperability
This level of healthcare interoperability is used for defining the syntax for data exchange. It helps the receiving information system to comprehend the data at the field level.
● Semantic Interoperability
Semantic interoperability is one of the most substantial levels in healthcare systems. The level allows the information systems to exchange and entirely interpret the received data. The high demand for this level is due to its ability to exchange the patient’s data through electronic mediums between authorized users.
● Organizational Interoperability
This level of interoperability adds various non-technical components to the system. The components consist of social and organizational aspects along with different exchange policies. Using these aspects, interoperability is integrated within organizational workflows. Together with other technical levels, a seamless data exchange between different healthcare organizations is established.
How Healthcare Interoperability Benefits Your Hospital Growth?
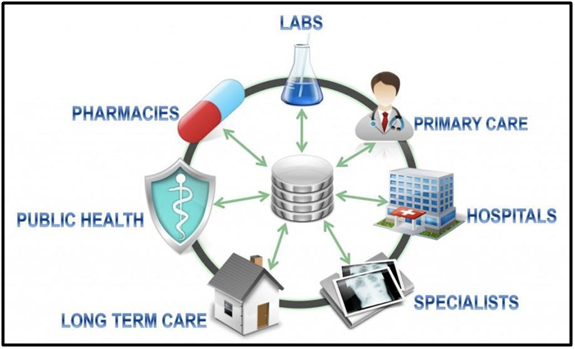
Source: Carecloud.com
Whether it is your digital healthcare software or hospital management software, integration of interoperability in them can bring a huge positive transformation to the workflow of your hospital. Let us get acquainted with some of the major benefits of using this system.
● Time Saving in Business and Administrative Processes
High time consumption to carry out numerous medical operations is one of the biggest challenges faced by hospitals. With the integration of interoperability, accessibility to health information of the patients will get faster. It will eliminate the need for time-consuming tasks such as processing intake information, co-ordination between the teams, etc.
● Enhanced Patient Safety and Satisfaction
The insights generated through these information systems are incredibly efficient in disclosing the complete picture of a patient’s health. It gives access to disparate data that helps medical practitioners to make more informed decisions based on the patient’s medical history and preferences.
In addition, it reduces adverse events, duplicate testing and helps conduct appropriate follow-up for the patients with appropriate care management.
● Better Collaborations
Interoperability creates a well-coordinated care system within the entire healthcare organization. This helps in getting easier and faster access to patient’s records which helps doctors to provide more accurate treatment to the patients.
● Value-Based Care
Providing value-based care to patients is the future of the digital healthcare sector. By integrating systems such as interoperability, different types of patient data are incorporated into the medical system. This includes non-traditional health data such as housing stability, food security status, and access to reliable transportation.
Understanding the patient’s health records according to this non-traditional health data can greatly improve the precision of diagnostics, and patients will get the required more refined treatment.
● Cost Efficiency with Deliverance of Better Quality
Interoperability efficiently eliminates various administrative and data validation tasks that enable medical staff to deliver technology-enabled values to the patient resulting in low treatment cost with increased quality.
● More Financial Stability
The amount of financial savings that are done with the use of hospital management software determines how effective the use of technology can be for stabilizing the finances of an organization. When interoperability is integrated into your system, the relationship between patient outcomes and financial performance gets amplified, offering more stability to your organization.
Steps that can be Taken to Improve Interoperability
The use of the following steps will help your organization to achieve better interoperability:
- Use a health information exchange (HIE) system while diagnosing the patient.
- Make use of neuro-linguistic programming and voice recognition in your system.
- Move to a single integrated EHR platform.
- Integrate workflows with point-of-care images.
- Add excessive data and other workloads to the cloud.
- Invest in content-enabled EHR with the expanded patient records.
- Get an efficient and robust digital healthcare software for your hospital or clinic.
Wrapping Up
With ongoing digitization in healthcare, interoperability will continue to evolve and provide multiple benefits to everyone in the healthcare sector. By bringing together people, processes, and technology, interoperability streamlines capturing of information, its interpretation, and the application of data that facilitates the need of all.
